{"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getarticle:\"{\\\"articleId\\\":434,\\\"categoryId\\\":2237}\"":{"body":{"Id":434,"FriendlyId":"","ArticleTypeId":0,"Title":"How do I set up host records for a domain?","ArticleName":"How do I set up host records for a domain?","ArticleSummary":"\r\n\t\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\" style=\"line-height:1.38;margin-top:0pt;margin-bottom:0pt;\" id=\"docs-internal-guid-b491ea00-b329-c1ea-717c-9c4bf6481fc4\">\r\n\t\t\t\t\u003cspan style=\"font-size:15.333333333333332px;font-family:Arial;color:#000000;background-color:#ffffff;font-weight:400;font-style:normal;font-variant:normal;text-decoration:none;vertical-align:baseline;\">\r\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\u003cbr />\r\n\t\t\t\t\u003c/span>\r\n\t\t\u003c/p>\r\n","PreponedSummary":false,"Approved":true,"Body":"DQoJCTxkaXY+VGhlIDxiPkhvc3QgUmVjb3JkczwvYj4gc2VjdGlvbiBpcyBhdmFpbGFibGUgb25seSBmb3IgdGhlIGRvbWFpbnMgdXNpbmcgTmFtZWNoZWFwIEJhc2ljRE5TLCBGcmVlRE5TIG9yIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc2VjdXJpdHkvcHJlbWl1bWRucy8iPlByZW1pdW1ETlM8L2E+LiA8YnIgLz48L2Rpdj4NCgkJPGRpdj4NCgkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJPC9kaXY+DQoJCTxkaXY+VG8gY2hlY2sgd2hpY2ggbmFtZXNlcnZlcnMgeW91ciBkb21haW4gaXMgdXNpbmcsIGdvIHRvIHlvdXIgTmFtZWNoZWFwIGRhc2hib2FyZCB1bmRlciA8Yj5Eb21haW4gTGlzdDwvYj4uIENsaWNrIG9uIDxzcGFuIGRhdGEtc3RhcnQ9IjMwNyIgZGF0YS1lbmQ9IjMxOSI+PGI+TWFuYWdlPC9iPiB1PC9zcGFuPm5kZXIgdGhlPGI+PC9iPjxzcGFuIGRhdGEtc3RhcnQ9IjMzNCIgZGF0YS1lbmQ9IjM0NiI+PGI+RG9tYWluPC9iPjwvc3Bhbj4gdGFiLDxzdHJvbmcgZGF0YS1zdGFydD0iMzA3IiBkYXRhLWVuZD0iMzE5Ij48L3N0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBkYXRhLXN0YXJ0PSIzMDciIGRhdGEtZW5kPSIzMTkiPm5leHQgdG8gdGhlIGRvbWFpbiBpbiBxdWVzdGlvbiBhbmQgPC9zcGFuPnNjcm9sbCBkb3duIHRvIHRoZSA8c3BhbiBkYXRhLXN0YXJ0PSIzNzEiIGRhdGEtZW5kPSIzODgiPjxiPk5hbWVzZXJ2ZXJzPC9iPjwvc3Bhbj4gc2VjdGlvbi4gVGhpcyB3aWxsIHNob3cgd2hldGhlciB5b3UncmUgdXNpbmcgTmFtZWNoZWFwJ3MgZGVmYXVsdCBuYW1lc2VydmVycyBvciBjdXN0b20gKHRoaXJkLXBhcnR5KSBuYW1lc2VydmVycy48L2Rpdj4NCgkJPGRpdj4NCgkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJPC9kaXY+DQoJCTxkaXY+SWbCoCB5b3Ugc2VlIG5vIG9wdGlvbiB0byBtYW5hZ2UgdGhlIEROUyByZWNvcmRzIGluIHRoZSBBZHZhbmNlZCBETlMgc2VjdGlvbiwgPHNwYW4gaWQ9ImFydGljbGUiPnlvdXIgZG9tYWluIGlzIHBvaW50ZWQgdG/CoCBhIHRoaXJkLXBhcnR5IG5hbWVzZXJ2ZXJzIE9SIG91ciBob3N0aW5nIG5hbWVzZXJ2ZXJzICg8aT5kbnMxLm5hbWVjaGVhcGhvc3RpbmcuY29tLCBkbnMyLm5hbWVjaGVhcGhvc3RpbmcuY29tPC9pPikuIEhlbmNlLCB5b3UgbmVlZCB0byBhZGQvdXBkYXRlIHRoZSBETlMgcmVjb3JkcyBhdCB5b3VyIGN1cnJlbnQgRE5TIHByb3ZpZGVyIG9yIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC85MjU2LzI5L2hvdy10by1lZGl0LWRucy16b25lLWluLWNwYW5lbC8iPmluIHlvdXIgY1BhbmVsPC9hPi48L3NwYW4+PC9kaXY+DQoJCTxkaXY+DQoJCQkJPHNwYW4gaWQ9ImFydGljbGUiPg0KCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJPC9zcGFuPg0KCQk8L2Rpdj4NCgkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCTxkaXY+VG8gc2V0IHVwIGhvc3QgcmVjb3JkcyBmb3IgeW91ciBkb21haW4gaW4gPGI+QWR2YW5jZWQgRE5TPC9iPiwgdXNlIHRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgaW5zdHJ1Y3Rpb25zPGk+OjwvaT48L2Rpdj4NCgkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCTxiciAvPjEuIFNpZ24gaW50byB5b3VyIDxiPk5hbWVjaGVhcCBhY2NvdW50PC9iPi48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4yLiBTZWxlY3QgPGI+RG9tYWluIExpc3Q8L2I+IGZyb20gdGhlIGxlZnQgc2lkZWJhciBhbmQgY2xpY2sgPGI+TWFuYWdlPC9iPiBuZXh0IHRvIHlvdXIgZG9tYWluOjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxkaXY+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL25jdHV0bWFuYWdlLnBuZyIgLz48L2Rpdj48ZGl2PjxiciAvPjwvZGl2PjxkaXY+My4gU2VsZWN0IHRoZSA8Yj5BZHZhbmNlZCBETlM8L2I+IHRhYiBhdCB0aGUgdG9wIG9mIHRoZSBwYWdlOg0KPC9kaXY+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2FkdmFuY2VkX2Rucy5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+NC4gSW4gdGhlIDxiPkhvc3QgUmVjb3JkczwvYj4gc2VjdGlvbiwgY2xpY2sgdGhlIDxiPkFkZCBOZXcgUmVjb3JkPC9iPiBidXR0b24gKDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8zMjMvNDYvd2h5LWNhbnQtaS1tb2RpZnktZW1haWwtZG9tYWluLXJlZGlyZWN0LWFuZC1ob3N0LXJlY29yZHMtaW4tbXktbmFtZWNoZWFwLWFjY291bnQvIj5jYW5ub3QgZWRpdCBIb3N0IFJlY29yZHM/PC9hPik6PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2FkZG5ld3JlY29yZC5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+SG9zdDo8L2I+IElmIHlvdSBuZWVkIHRvIGNyZWF0ZSBhIHJlY29yZCBmb3IgYSBiYXJlIGRvbWFpbiAoZS5nLiwgPGk+bXlkb21haW4udGxkPC9pPiksIGl0IGlzIG5lZWRlZCB0byBwdXQgPGI+QDwvYj4gaW4gdGhpcyBmaWVsZC48YnIgLz5JbiBjYXNlIHlvdSBuZWVkIHRvIGNyZWF0ZSBhIHJlY29yZCBmb3IgYW55IHN1YmRvbWFpbiAobGlrZSB3d3cuPGk+bXlkb21haW4udGxkIDwvaT5vciA8aT5ibG9nLjwvaT48aT5teWRvbWFpbi50bGQ8L2k+KSBzaG91bGQgYmUgY3JlYXRlZCwgcHV0IDxiPm9ubHkgPC9iPnRoZSBuYW1lIG9mIHlvdXIgc3ViZG9tYWluIGludG8gdGhlIEhvc3QgZmllbGQgd2l0aG91dCBhZGRpbmcgdGhlIGRvbWFpbiBpdHNlbGYuIFRodXMsIHRoZSByZWNvcmQgZm9yIHd3dy48aT5teWRvbWFpbi50bGQgPC9pPnNob3VsZCBoYXZlIG9ubHkgPGI+d3d3IDwvYj5pbiB0aGUgSG9zdDogDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvaG9zdHNfYWQucG5nIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiPlRUTDogPC9iPlRoZSBUVEwgdmFsdWUgb2YgMTgwMCBzZWNvbmRzICgzMCBtaW51dGVzKSBtZWFucyB0aGF0LCBpZiBhIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vZG5zL3doYXQtaXMtZG5zLWRvbWFpbi1uYW1lLXN5c3RlbS1kZWZpbml0aW9uLyI+RE5TPC9hPiByZWNvcmQgd2FzIGNoYW5nZWQgb24gbmFtZXNlcnZlcnMsIEROUyBzZXJ2ZXJzIGFyb3VuZCB0aGUgd29ybGQgY2FuIHN0aWxsIGJlIHNob3dpbmcgdGhlIG9sZCB2YWx1ZSBmcm9tIHRoZWlyIGNhY2hlIGZvciB1cCB0byAzMCBtaW51dGVzIGFmdGVyIHRoZSBjaGFuZ2UuPGJyIC8+T3VyIGRlZmF1bHQgVFRMIGlzIDMwIG1pbnV0ZXMgKDUgbWludXRlcyBmb3IgQUxJQVMgcmVjb3JkcykuIFlvdSBjYW4gc2VsZWN0IGl0IGZyb20gdGhlIGRyb3AtZG93biBvciBqdXN0IGxlYXZlIGl0ICJBdXRvbWF0aWMiLjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPkhlcmUgYXJlIHRoZSB0eXBlcyBvZiByZWNvcmRzIHRoYXQgY2FuIGJlIGNyZWF0ZWQgb24gb3VyIEROUyBzZXJ2ZXJzLCBhbG9uZyB3aXRoIGEgYnJpZWYgZGVzY3JpcHRpb24gb2YgZWFjaDo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48dGFibGUgY2xhc3M9Ik1zb05vcm1hbFRhYmxlIiBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLWNvbGxhcHNlOiBjb2xsYXBzZTsiIGNlbGxzcGFjaW5nPSIwIiBjZWxscGFkZGluZz0iMCIgYm9yZGVyPSIwIj48dGJvZHk+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyOiAxcHQgc29saWQgd2luZG93dGV4dDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cCBzdHlsZT0idGV4dC1hbGlnbjogY2VudGVyOyIgYWxpZ249ImNlbnRlciI+PGI+QWRkcmVzcyBSZWNvcmQgVHlwZTwvYj48L3A+PC90ZD48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogc29saWQgc29saWQgc29saWQgbm9uZTsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiB3aW5kb3d0ZXh0IHdpbmRvd3RleHQgd2luZG93dGV4dCAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IDFwdCAxcHQgMXB0IG1lZGl1bTsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cCBzdHlsZT0idGV4dC1hbGlnbjogY2VudGVyOyIgYWxpZ249ImNlbnRlciI+PGI+RGVzY3JpcHRpb248L2I+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cD48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzMxOS8yMjM3L2hvdy1jYW4taS1zZXQtdXAtYW4tYS1hZGRyZXNzLXJlY29yZC1mb3ItbXktZG9tYWluIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iQSAoQWRkcmVzcykiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX3BhcmVudCI+QSAoQWRkcmVzcyk8L2E+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPkFsbG93cyB5b3UgdG8gYXNzb2NpYXRlIGEgaG9zdCB3aXRoIGFuIElQdjQgYWRkcmVzcy4gVGhlIElQIGFkZHJlc3MgdGhhdCB5b3UgdXNlIGRvZXMgbm90IGhhdmUgdG8gYmUgb24geW91ciBuZXR3b3JrLiA8L3NwYW4+PC9wPjxwPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5Gb3IgZXhhbXBsZSwgPC9zcGFuPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij55b3UgY2FuIGhhdmUgdGhlIGhvc3QgcmVjb3JkIGZvciB3d3cgcG9pbnRlZCB0byAyMDcuNDYuMTMwLjE0ICh0aGUgYWRkcmVzcyBmb3IgdGhlIE1pY3Jvc29mdCB3ZWJzaXRlKS4gPC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8zMTkvMjIzNy9ob3ctY2FuLWktc2V0LXVwLWFuLWEtYWRkcmVzcy1yZWNvcmQtZm9yLW15LWRvbWFpbiIgbGlua3RleHQ9IkFBQUEgKElQdjYpIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+QUFBQSAoSVB2Nik8L2E+PGJyIC8+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPkFsbG93cyB5b3UgdG8gYXNzb2NpYXRlIGEgaG9zdCB3aXRoIGFuIElQdjYgYWRkcmVzcy4gVGhlIElQIGFkZHJlc3MgdGhhdCB5b3UgdXNlIGRvZXMgbm90IGhhdmUgdG8gYmUgb24geW91ciBuZXR3b3JrLiA8L3NwYW4+PC9wPjxwPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5Gb3IgZXhhbXBsZSw8L3NwYW4+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPiB5b3UgY2FuIGhhdmUgdGhlIGhvc3QgcmVjb3JkIGZvciB3d3cgcG9pbnRlZCB0byAyMDAxOjBkYjg6MTFhMzowOWQ3OjFmMzQ6OGEyZTowN2EwOjc2NWQ8YnIgLz48L3NwYW4+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cD48c3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogbm9ybWFsOyBmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij48YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvMzIyLzIyMzcvaG93LWNhbi1pLXNldC11cC1teC1yZWNvcmRzLXJlcXVpcmVkLWZvci1tYWlsLXNlcnZpY2UiIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJNWEUgKE1haWwgRWFzeSkiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5NWEUgKE1haWwgRWFzeSk8L2E+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPkFsbG93cyB5b3UgdG8gc3BlY2lmeSB0aGUgYWRkcmVzcyBvZiB5b3VyIG1haWwgc2VydmVyLiBXaGVuIHlvdSB1c2UgYSBtYWlsIHJlY29yZCwgeW91IG11c3QgdXNlIGFuIElQIGFkZHJlc3MgaW4gdGhlIGFkZHJlc3MgZmllbGQuIDwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PHA+PGI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPk5vdGUgdG8gcHJvZmVzc2lvbmFsIHVzZXJzOjwvc3Bhbj48L2I+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPiBDcmVhdGluZyBhIG1haWwgcmVjb3JkIGFjdHVhbGx5IGNyZWF0ZXMgYm90aCB0aGUgTVggYW5kIEEgcmVjb3JkcyBpbiBETlMuIEFsc28sIHdoZW4gdXNpbmcgbXVsdGlwbGUgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXJzLCBhIHByZWZlcmVuY2UgdmFsdWUgb2YgMTAgaXMgdXNlZCBvbiBhbGwgZW50cmllcy4gPC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzMyMi8yMjM3L2hvdy1jYW4taS1zZXQtdXAtbXgtcmVjb3Jkcy1yZXF1aXJlZC1mb3ItbWFpbC1zZXJ2aWNlIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iTVggKE1haWwpIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+TVggKE1haWwpPC9hPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij48L3NwYW4+PC9zdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PC90ZD48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZCBub25lOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQgbWVkaXVtOyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyMjMsIDIyMywgMjQ1KSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5NWCAoTWFpbCk8L3NwYW4+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4gY2FuIGJlIGVpdGhlciBhIGhvc3QgbmFtZSB1bmRlciB5b3VyIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIChmb3IgZXhhbXBsZTxpPiwgbWFpbDM8L2k+KSwgb3IgdGhlIG5hbWUgb2YgYSBtYWlsIHNlcnZlciAoZm9yIGV4YW1wbGU8aT4sIG1haWwueWFob28uY29tPC9pPikuIDwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPldoZW4gdXNpbmcgYSBtYWlsIHNlcnZlciBuYW1lLCBpdCBzaG91bGQgZW5kIHdpdGggYSBwZXJpb2QgKCIuIikuIElmIHlvdSBmb3JnZXQgdG8gYWRkIGl0LCB0aGUgc3lzdGVtIHdpbGwgZG8gaXQgYXV0b21hdGljYWxseS4gPGJyIC8+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4Lzk2NDYvMjIzNy9ob3ctY2FuLWktc2V0LXVwLWEtY25hbWUtcmVjb3JkLWZvci1teS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJDTkFNRSAoQWxpYXMpIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+Q05BTUU8L2E+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPklzIHVzZWQgdG8gYXNzb2NpYXRlIGEgaG9zdCBuYW1lIHdpdGggYW5vdGhlciBob3N0LiBUaGUgaG9zdCB0aGF0IHlvdSB3aXNoIHRvIHBvaW50IHRvIGRvZXMgbm90IGhhdmUgdG8gYmUgb24geW91ciBuZXR3b3JrLiA8L3NwYW4+PC9wPjxwPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5QbGVhc2UgZG9uJ3Qgc2V0IHVwIENOQU1FIGZvciBhIG5ha2VkIGRvbWFpbiAoQCBob3N0bmFtZSkgc2luY2UgaXQgbWF5IGFmZmVjdCB0aGUgb3BlcmF0aW9uIG9mIHRoZSBkb21haW4ncyBNWCByZWNvcmRzIGFuZCwgY29uc2VxdWVudGx5LCB0aGUgZW1haWwgc2VydmljZS48YnIgLz48L3NwYW4+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cD48c3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogbm9ybWFsOyBmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5OUzwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48L3A+PC90ZD48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZCBub25lOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQgbWVkaXVtOyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyMjMsIDIyMywgMjQ1KSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5BcmUgcHJpbWFyaWx5IHVzZWQgaWYgeW91IHdhbnQgdG8gZGl2aWRlIHlvdXIgZG9tYWluIGludG8NCnN1YmRvbWFpbnMuIDxiciAvPjxiciAvPlN1YmRvbWFpbnMgaW5kaWNhdGUgdGhhdCB5b3UgYXJlIGRlbGVnYXRpbmcgYSBwb3J0aW9uIG9mIGEgZG9tYWluIG5hbWUgdG8gYSBkaWZmZXJlbnQgZ3JvdXAgb2YgbmFtZXNlcnZlcnMsIHRodXMgY3JlYXRpbmcgTlMgcmVjb3JkcyB0byBwb2ludCB0aGUgaG9zdG5hbWUgKG5hbWUgb2YgdGhlIHN1YmRvbWFpbikgdG8gZGlmZmVyZW50IG5hbWUgc2VydmVycy48L3NwYW4+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyNDYsIDI0NiwgMjUyKSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8zODUvMjIzNy9ob3ctZG8taS1zZXQtdXAtYS11cmwtcmVkaXJlY3QtZm9yLWEtZG9tYWluIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iVVJMIFJlZGlyZWN0IiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+VVJMIFJlZGlyZWN0PC9hPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij48L3NwYW4+PC9zdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PC90ZD48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZCBub25lOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQgbWVkaXVtOyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyNDYsIDI0NiwgMjUyKSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5TdGFuZGFyZCBtZXRob2QgZm9yIFVSTCBGb3J3YXJkaW5nLiBXaGVuIHVzZXJzIHR5cGUgaW4geW91ciBkb21haW4gbmFtZSwgdGhleSBhcmUgcmVkaXJlY3RlZCB0byB0aGUgd2ViIHNlcnZlciB0aGF0IGhvc3RzIHlvdXIgcGFnZXMuIDwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPk9uZSBkcmF3YmFjayBvZiB0aGlzIG9wdGlvbiBpcyB0aGF0IHRoZSBicm93c2VyIHdpbGwgZGlzcGxheSB0aGUgVVJMIHRoYXQgaXMgb24gdGhlIGFjdHVhbCB3ZWIgcGFnZSwgbm90IHlvdXIgZG9tYWluIG5hbWUuIDxiciAvPjwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPllvdSBjYW4gcHJldmVudCB0aGlzIGJ5IHVzaW5nIHRoZSBVUkwgRnJhbWUgbWV0aG9kIGluc3RlYWQgKHNlZSBiZWxvdykuIDwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyMjMsIDIyMywgMjQ1KSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8zODUvMjIzNy9ob3ctZG8taS1zZXQtdXAtYS11cmwtcmVkaXJlY3QtZm9yLWEtZG9tYWluIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iVVJMIFJlZGlyZWN0ICgzMDEpIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+VVJMIFJlZGlyZWN0ICgzMDEpPC9hPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48L3A+PHA+PGJyIC8+KEF2YWlsYWJsZSBvbiBCYXNpY0ROUywgRnJlZUROUyBhbmQgUHJlbWl1bUROUyBvbmx5KTwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPlByZWZlcnJlZCB3YXkgdG8gcmVkaXJlY3QgVVJMcyBzaW5jZSBpdCBpbmZvcm1zIHNlYXJjaCBlbmdpbmVzIHRoYXQgdGhlIFVSTCBoYXMgbW92ZWQgcGVybWFuZW50bHkuIFRoZSBuZXcgVVJMIHBhZ2Ugc2hvdWxkIHRoZW4gYmUgc2hvd24gaW5zdGVhZCBvZiB0aGUgb2xkIFVSTCBpbiB0aGUgc2VhcmNoIHJlc3VsdHMsIHdoaWxlIHN0aWxsIG1haW50YWluaW5nIHRoZSBwYWdlIHJhbmsgb2YgdGhlIG9sZCBVUkwuPGJyIC8+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzM4NS8yMjM3L2hvdy1kby1pLXNldC11cC1hLXVybC1yZWRpcmVjdC1mb3ItYS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJVUkwgRnJhbWUiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5VUkwgRnJhbWU8L2E+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPlNpbWlsYXIgdG8gVVJMIFJlZGlyZWN0IGV4Y2VwdCB0aGF0IGluc3RlYWQgb2YgcmVkaXJlY3RpbmcgdGhlIGNsaWVudCB0byB5b3VyIHdlYiBwYWdlLCB0aGUgd2ViIHBhZ2UgaXMgZGlzcGxheWVkIGluIGEgZnJhbWUgZnJvbSBvdXIgd2ViIHNlcnZlci4gPC9zcGFuPjwvcD48cD48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+V2l0aCB0aGlzIG9wdGlvbiwgdGhlIGJyb3dzZXIgd2lsbCBkaXNwbGF5IHlvdXIgZG9tYWluIG5hbWUgKGZvciBleGFtcGxlPGk+LCB3d3cueW91cmRvbWFpbi50bGQ8L2k+KSBhbmQgbm90IHRoZSBhY3R1YWwgVVJMIG9mIHRoZSBwYWdlJ3MgaG9zdCAoZm9yIGV4YW1wbGU8aT4sIGh0dHA6Ly9ob21lLmluZm9zcGFjZS5jb20vdXNlcjMzPC9pPikuPC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvNTk3LzIyMzcvaG93LWNhbi1pLXNldC11cC1hLWNhdGNoYWxsLXdpbGRjYXJkLXN1YmRvbWFpbiIgbGlua3RleHQ9IldpbGRjYXJkIHJlY29yZCIgbGlua3R5cGU9IkN1c3RvbSIgdGFyZ2V0PSJfYmxhbmsiPldpbGRjYXJkIHJlY29yZDwvYT48L3NwYW4+PC9zdHJvbmc+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij48L3NwYW4+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQgbm9uZTsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0IG1lZGl1bTsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cD48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+VGhlIHN0YXIgKiByZWNvcmQgaXMgYSB3aWxkY2FyZCByZWNvcmQgd2hpY2ggaXMgdXNlZCB0byBpbmNsdWRlIGFueSByZWNvcmRzIG9yIHN1YmRvbWFpbnMgdGhhdCB5b3UgaGF2ZSBub3Qgc3BlY2lmaWVkIHRvIGNhdGNoIHR5cG9zIG9yIG1pc3Rha2VzLjwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyNDYsIDI0NiwgMjUyKSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8zMTgvMjIzNy9jYW4taS1hZGQtYW4tc3J2LXJlY29yZC1mb3ItbXktZG9tYWluIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iU1JWIHJlY29yZCIgbGlua3R5cGU9IkN1c3RvbSIgdGFyZ2V0PSJfYmxhbmsiPlNSViByZWNvcmQ8L2E+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPlNlcnZpY2UgcmVjb3JkIGlzIGEgc3BlY2lmaWNhdGlvbiBvZiBkYXRhIGluIHRoZSBEb21haW4gTmFtZSBTeXN0ZW0gZGVmaW5pbmcgdGhlIGxvY2F0aW9uIChpLmUuLCB0aGUgcG9ydCBudW1iZXIpIG9mIHNlcnZlcnMgZm9yIHNwZWNpZmllZCBzZXJ2aWNlcyAoZS5nLiwgPGk+TWluZWNyYWZ0PC9pPikuIDwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyMjMsIDIyMywgMjQ1KSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij48YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvMzE3LzIyMzcvaG93LWRvLWktYWRkLXR4dHNwZmRraW1kbWFyYy1yZWNvcmRzLWZvci1teS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJUWFQgcmVjb3JkIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+VFhUIHJlY29yZDwvYT48L3NwYW4+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3N0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+PHA+UHJvdmlkZXMgdGhlIGFiaWxpdHkgdG8gYXNzb2NpYXRlIHNvbWUgdGV4dCB3aXRoIGEgaG9zdCBvciBvdGhlciBuYW1lLiBNYW55IFRYVCByZWNvcmRzIGNhbiBiZSBhZGRlZCBmb3IgYSBmdWxseSBxdWFsaWZpZWQgZG9tYWluIG5hbWUuIDxiciAvPjxiciAvPlVzdWFsbHkswqAgVFhUIHJlY29yZCBpcyB1c2VkIGZvciBTUEYgKFNlbmRlciBQb2xpY3kgRnJhbWV3b3JrKSwgREtJTSAoRG9tYWluS2V5cyBJZGVudGlmaWVkIEUtbWFpbCkgYW5kIERNQVJDIChEb21haW4tYmFzZWQgTWVzc2FnZSBBdXRoZW50aWNhdGlvbiwgUmVwb3J0aW5nIGFuZCBDb25mb3JtYW5jZSkgcHVycG9zZXMuIFRYVCByZWNvcmRzIHdlcmUgb3JpZ2luYWxseSBkZXZlbG9wZWQgdG8gY29udGFpbiBodW1hbiByZWFkYWJsZSBpbmZvcm1hdGlvbiBhYm91dCBhIGRvbWFpbiBvciBzZXJ2ZXIuPGJyIC8+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjwvc3Bhbj48L3A+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyNDYsIDI0NiwgMjUyKSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPjxwPjxzdHJvbmc+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPjxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC85OTkxLzM4L2NhYS1yZWNvcmQtYW5kLXdoeS1pdC1pcy1uZWVkZWQtc3NsLXJlbGF0ZWQiIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJDQUEgcmVjb3JkIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+Q0FBIHJlY29yZDwvYT48L3NwYW4+PC9zdHJvbmc+PHN0cm9uZz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvc3Ryb25nPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij48L3NwYW4+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQgbm9uZTsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0IG1lZGl1bTsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cD48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+Q2VydGlmaWNhdGlvbiBBdXRob3JpdHkgQXV0aG9yaXphdGlvbiAoQ0FBKSBpcyBhIEROUyByZWNvcmQsIHdoaWNoIGFsbG93cyBhIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIGhvbGRlciB0byBzcGVjaWZ5IHRoZSBwcmVmZXJyZWQgQ2VydGlmaWNhdGlvbiBBdXRob3JpdGllcyAoQ0FzKSB0byBpc3N1ZSBjZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZXMgZm9yIHRoYXQgZG9tYWluLCBoZW5jZSBtYWtpbmcgbm8gb3RoZXIgQ0FzIGF1dGhvcml6ZWQgdG8gZG8gdGhhdC4gTW9yZSBpbmZvcm1hdGlvbiBjYW4gYmUgZm91bmQgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4Lzk5OTEvMzgvY2FhLXJlY29yZC1hbmQtd2h5LWl0LWlzLW5lZWRlZC1zc2wtcmVsYXRlZCIgbGlua3RleHQ9ImhlcmUiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5oZXJlPC9hPi48L3NwYW4+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj48cD48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzEwMTI4LzIyMzcvaG93LXRvLWNyZWF0ZS1hbi1hbGlhcy1yZWNvcmQiIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJBTElBUyByZWNvcmQiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5BTElBUyAoQU5BTUUpIHJlY29yZDwvYT48YnIgLz48L3NwYW4+PC9wPjwvdGQ+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQgbm9uZTsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0IG1lZGl1bTsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj5JdCBpcyBhIHZpcnR1YWwgaG9zdCByZWNvcmQgdHlwZSB3aGljaCBpcyB1c2VkIHRvIHBvaW50IG9uZSBkb21haW4gbmFtZSB0byBhbm90aGVyIG9uZSwgYWxtb3N0IHRoZSBzYW1lIGFzIENOQU1FLiBCdXQgdGhlIGltcG9ydGFudCBkaWZmZXJlbmNlIGhlcmUgaXMgdGhhdCBBTElBUyBjYW4gY29leGlzdCB3aXRoIG90aGVyIHJlY29yZHMgb24gdGhhdCBuYW1lLiA8YnIgLz5BbiBBTElBUyByZWNvcmQgY2FuIGFsc28gYmUgdXNlZCBpZiB5b3Ugd2lzaCB0byBhbGlhcyB0aGUgcm9vdCBkb21haW4gdG8gYW5vdGhlciBzZXJ2aWNlICh3aGljaCBpcyBpbXBvc3NpYmxlIHdpdGggdGhlIGhlbHAgb2YgYSBDTkFNRSByZWNvcmQpLiA8YnIgLz48L3RkPjwvdHI+PC90Ym9keT48L3RhYmxlPjxwPjxiciAvPjwvcD48c3Ryb25nIGlkPSJkb2NzLWludGVybmFsLWd1aWQtNjI1MTJhNDQtOGUxNi0yZTgzLTBkNzItZWU3NTBiM2FmMTcwIj48L3N0cm9uZz48cCBhbGlnbj0iY2VudGVyIj5UaGF0J3MgaXQhICANCklmIHlvdSBoYXZlIGFueSBxdWVzdGlvbnMgb3IgbmVlZCBhc3Npc3RhbmNlLCBvdXIgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2xpdmUtY2hhdC9kb21haW5zLmFzcHgiIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5TdXBwb3J0IFRlYW08L2E+IGlzIGF2YWlsYWJsZSAyNC83IHRvIGhlbHAgeW91LjwvcD4=","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"2025-04-14T10:16:08.0000000","LiveDateTime":"1754-02-02T00:00:00.0000000","CreatedDateTime":"2008-08-11T08:48:39.0000000","ApprovalDatetime":"2008-08-22T06:16:56.0000000","RequestCount":294459,"MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false,"RatingValue":3,"CategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"}],"AssociatedCategories":[{"CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup","CategoryDisplayName":"DomainsHost records setup"}],"AssociatedTags":[],"RelatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":535,"PreferedCategoryId":51,"ArticleTypeId":0,"ArticleName":"What type of DNS records can I manage?","ArticleTypeName":null,"Title":"What type of DNS records can I manage?","LiveDateTime":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/06/2022","MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false}],"AssociatedMedias":[],"PreferredCategoryId":0,"RootParentCategoryName":"","RootParentCategoryId":0},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategorybycategoryid:\"{\\\"categoryId\\\":2237}\"":{"body":{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryDto","Description":"SWYgeW91ciBkb21haW4gaXMgcG9pbnRlZCB0byBvdXLCoEJhc2ljRE5TLCBQcmVtaXVtRE5TIG9yIA0KRnJlZUROUywgeW91IGNhbiBzZXQgdXAgQSwgQUFBQSwgQUxJQVMsIENOQU1FLCBOUywgU1JWLCBUWFQsIFVSTCBSZWRpcmVjdCwgTVgsIA0KTVhFLCBDQUEgcmVjb3JkcyBmcm9tIE5hbWVjaGVhcCdzIHNpZGUu","ParentCategoryId":34,"Parent_Category_Name":"Domains","FriendlyId":null,"ApprovedYN":true,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"CreatedDateTime":"06/27/2016 06:59:07","CurrentCategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"}],"RelatedCategories":[],"AssociatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":642,"Title":"DNS","ArticleName":"DNS","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/24/2020"},{"ArticleId":10128,"Title":"How to create an ALIAS record","ArticleName":"How to create an ALIAS record","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/09/2025"},{"ArticleId":434,"Title":"How do I set up host records for a domain?","ArticleName":"How do I set up host records for a domain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/14/2025"},{"ArticleId":579,"Title":"Which record type option should I choose for the information I’m about to enter?","ArticleName":"Which record type option should I choose for the information I’m about to enter?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/20/2025"},{"ArticleId":9776,"Title":"How to Create a Subdomain for my Domain","ArticleName":"How to Create a Subdomain for my Domain","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/24/2024"},{"ArticleId":320,"Title":"What is a catch-all (wildcard) subdomain?","ArticleName":"What is a catch-all (wildcard) subdomain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/15/2021"},{"ArticleId":597,"Title":"How can I set up a catch-all (wildcard) subdomain?","ArticleName":"How can I set up a catch-all (wildcard) subdomain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/14/2021"},{"ArticleId":319,"Title":"How can I set up an A (address) record for my domain?","ArticleName":"How can I set up an A (address) record for my domain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/23/2024"},{"ArticleId":384,"Title":"What is URL Redirect and how does it work?","ArticleName":"What is URL Redirect and how does it work?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/03/2021"},{"ArticleId":385,"Title":"How to set up a URL redirect for a domain","ArticleName":"How to set up a URL redirect for a domain","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/20/2025"},{"ArticleId":10043,"Title":"URL Redirect with Parameters","ArticleName":"URL Redirect with Parameters","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"05/05/2021"},{"ArticleId":9604,"Title":"Types of Domain Redirects - 301, 302 URL Redirects, URL Frame (and CNAME)","ArticleName":"Types of Domain Redirects - 301, 302 URL Redirects, URL Frame (and CNAME)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/14/2025"},{"ArticleId":9678,"Title":"How to redirect (sub)domain to a certain IP address along with a port?","ArticleName":"How to redirect (sub)domain to a certain IP address along with a port?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/14/2021"},{"ArticleId":313,"Title":"What is URL Frame?","ArticleName":"What is URL Frame?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"06/27/2016"},{"ArticleId":314,"Title":"How can I set up a URL Frame for my domain?","ArticleName":"How can I set up a URL Frame for my domain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/14/2021"},{"ArticleId":315,"Title":"What are URL Frame Meta Tags used for?","ArticleName":"What are URL Frame Meta Tags used for?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"06/27/2016"},{"ArticleId":9699,"Title":"How to set URL Frame Meta Tags for a domain","ArticleName":"How to set URL Frame Meta Tags for a domain","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/08/2021"},{"ArticleId":9646,"Title":"How to Create a CNAME Record For Your Domain","ArticleName":"How to Create a CNAME Record For Your Domain","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/23/2024"},{"ArticleId":317,"Title":"How do I add TXT/SPF/DKIM/DMARC records for my domain?","ArticleName":"How do I add TXT/SPF/DKIM/DMARC records for my domain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/14/2025"},{"ArticleId":318,"Title":"Can I add an SRV record for my domain?","ArticleName":"Can I add an SRV record for my domain?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/14/2021"},{"ArticleId":9461,"Title":"How should an SPF record look like?","ArticleName":"How should an SPF record look like?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/14/2021"},{"ArticleId":9736,"Title":"Consolidating several SPF records into one","ArticleName":"Consolidating several SPF records into one","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/13/2024"},{"ArticleId":322,"Title":"How can I set up MX records required for mail service?","ArticleName":"How can I set up MX records required for mail service?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/20/2025"},{"ArticleId":9623,"Title":"How to set up default domain and email redirects","ArticleName":"How to set up default domain and email redirects","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/13/2020"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":19574,"Tag":" set"},{"TagId":19994,"Tag":" create"},{"TagId":20139,"Tag":" forwarding"},{"TagId":21191,"Tag":" map"},{"TagId":21743,"Tag":" up"},{"TagId":24630,"Tag":" CNAME"},{"TagId":25167,"Tag":" records"},{"TagId":26421,"Tag":" domains"},{"TagId":27954,"Tag":" A"},{"TagId":27955,"Tag":" AAAA"},{"TagId":27956,"Tag":" NS"},{"TagId":27957,"Tag":" SRV"},{"TagId":27959,"Tag":" URL"},{"TagId":28746,"Tag":" txt"},{"TagId":68698,"Tag":"host"},{"TagId":68699,"Tag":" refirect"}],"CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategories:\"{\\\"parentCategoryId\\\":0,\\\"getTree\\\":true}\"":{"body":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/cloud-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2228,"CategoryName":"Apps","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/easywp-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2239,"CategoryName":"EasyWP","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2254,"CategoryName":"Domains How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2255,"CategoryName":"Hosting How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2257,"CategoryName":"Sales & Payments How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2258,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2262,"CategoryName":"EasyWP How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://download.namecheap.com/assets/img/domainvault-red@2x.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2289,"CategoryName":"Domain Vault","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/support-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":5,"CategoryName":"General & Support","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/savings-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2200,"CategoryName":"Checkout & Billing","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/reseller-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/protection-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":37,"CategoryName":"Domain Privacy Protection","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/status-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2209,"CategoryName":"Domain Transfers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/server-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/email-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/security-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/performance-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":9,"CategoryName":"My Account","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/affiliates-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":55,"CategoryName":"Affiliates","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/tools-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2211,"CategoryName":"API & Resellers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/timer-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2212,"CategoryName":"Legacy Products","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/premiumdns-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2231,"CategoryName":"PremiumDNS","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://static.nc-img.com/live-resource/icons/knowledgebase/fastVPN_icon-150px.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2265,"CategoryName":"FastVPN","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}],"status":200,"statusText":"OK"}}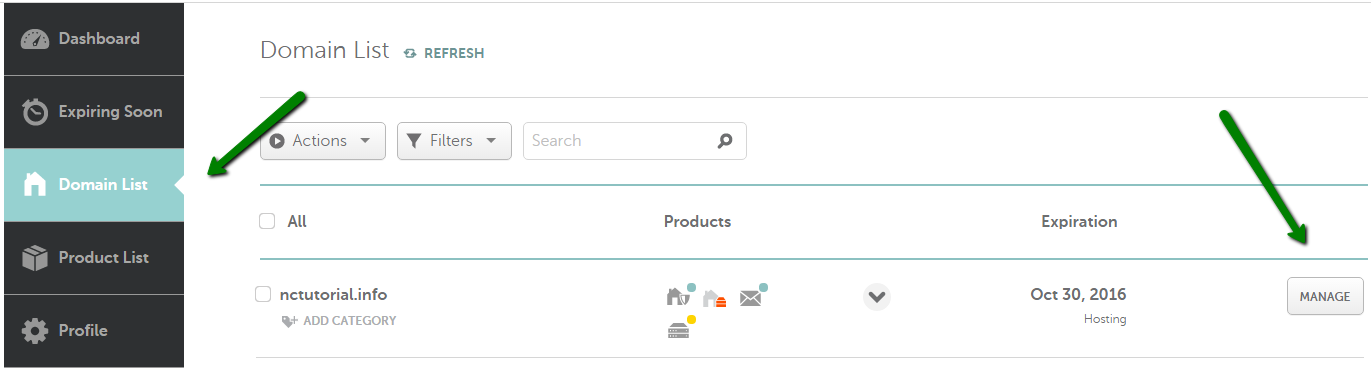
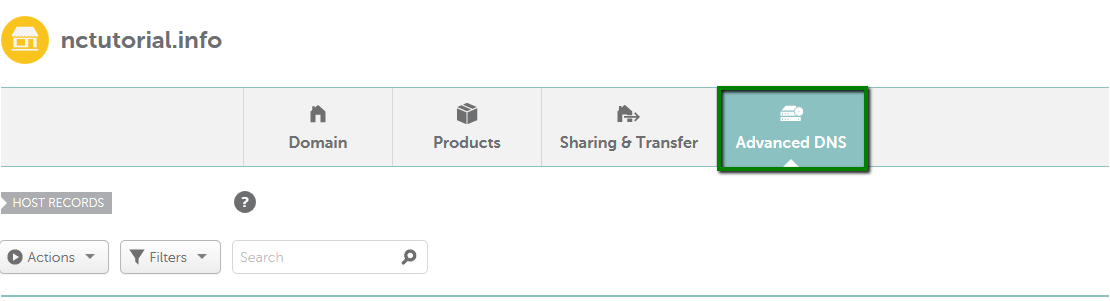
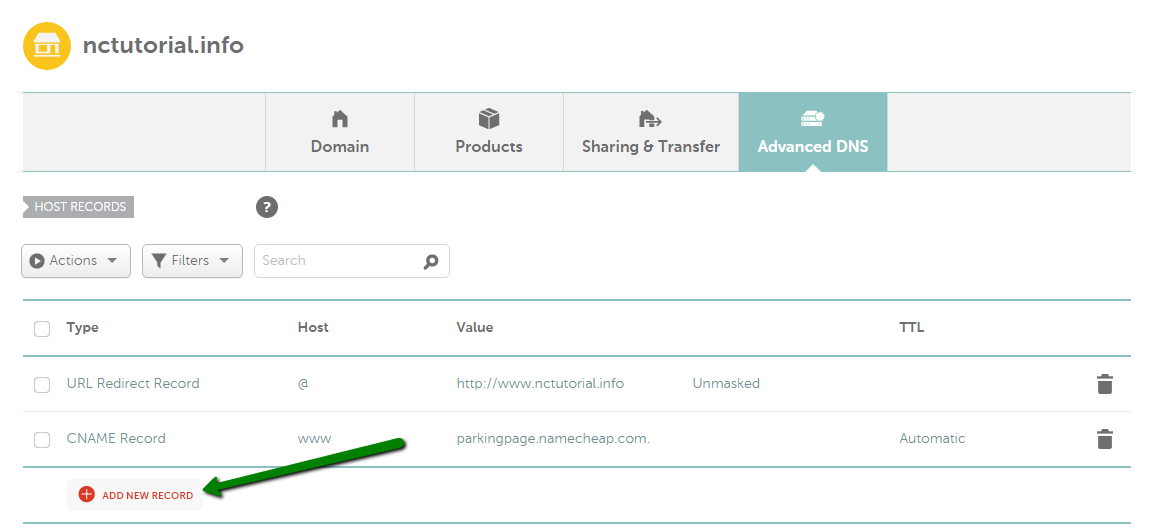
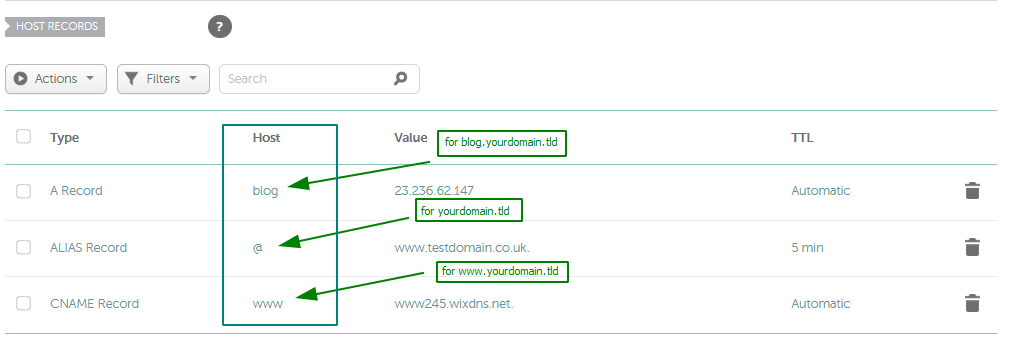
Address Record Type | Description |
Allows you to associate a host with an IPv4 address. The IP address that you use does not have to be on your network. For example, you can have the host record for www pointed to 207.46.130.14 (the address for the Microsoft website). | |
Allows you to associate a host with an IPv6 address. The IP address that you use does not have to be on your network. For example, you can have the host record for www pointed to 2001:0db8:11a3:09d7:1f34:8a2e:07a0:765d | |
Allows you to specify the address of your mail server. When you use a mail record, you must use an IP address in the address field. Note to professional users: Creating a mail record actually creates both the MX and A records in DNS. Also, when using multiple mail servers, a preference value of 10 is used on all entries. | |
MX (Mail) can be either a host name under your domain name (for example, mail3), or the name of a mail server (for example, mail.yahoo.com). When using a mail server name, it should end with a period ("."). If you forget to add it, the system will do it automatically. | |
Is used to associate a host name with another host. The host that you wish to point to does not have to be on your network. Please don't set up CNAME for a naked domain (@ hostname) since it may affect the operation of the domain's MX records and, consequently, the email service. | |
NS | Are primarily used if you want to divide your domain into
subdomains. Subdomains indicate that you are delegating a portion of a domain name to a different group of nameservers, thus creating NS records to point the hostname (name of the subdomain) to different name servers. |
Standard method for URL Forwarding. When users type in your domain name, they are redirected to the web server that hosts your pages. One drawback of this option is that the browser will display the URL that is on the actual web page, not your domain name. You can prevent this by using the URL Frame method instead (see below). | |
| Preferred way to redirect URLs since it informs search engines that the URL has moved permanently. The new URL page should then be shown instead of the old URL in the search results, while still maintaining the page rank of the old URL. |
Similar to URL Redirect except that instead of redirecting the client to your web page, the web page is displayed in a frame from our web server. With this option, the browser will display your domain name (for example, www.yourdomain.tld) and not the actual URL of the page's host (for example, http://home.infospace.com/user33). | |
The star * record is a wildcard record which is used to include any records or subdomains that you have not specified to catch typos or mistakes. | |
Service record is a specification of data in the Domain Name System defining the location (i.e., the port number) of servers for specified services (e.g., Minecraft). | |
Provides the ability to associate some text with a host or other name. Many TXT records can be added for a fully qualified domain name. | |
Certification Authority Authorization (CAA) is a DNS record, which allows a domain name holder to specify the preferred Certification Authorities (CAs) to issue certificates for that domain, hence making no other CAs authorized to do that. More information can be found here. | |
| It is a virtual host record type which is used to point one domain name to another one, almost the same as CNAME. But the important difference here is that ALIAS can coexist with other records on that name. An ALIAS record can also be used if you wish to alias the root domain to another service (which is impossible with the help of a CNAME record). |
That's it! If you have any questions or need assistance, our Support Team is available 24/7 to help you.
Need help? We're always here for you.