{"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getarticle:\"{\\\"articleId\\\":397,\\\"categoryId\\\":2194}\"":{"body":{"Id":397,"FriendlyId":"","ArticleTypeId":3,"Title":"How to clear local DNS cache","ArticleName":"How to clear local DNS cache","ArticleSummary":null,"PreponedSummary":true,"Approved":true,"Body":"DQoJCTxwPg0KVGhpcyBndWlkZSBkZXNjcmliZXMgaG93IHRvIGNsZWFyIGxvY2FsIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vZG5zL3doYXQtaXMtZG5zLWRvbWFpbi1uYW1lLXN5c3RlbS1kZWZpbml0aW9uLyI+RE5TPC9hPiBjYWNoZSBvbiBkaWZmZXJlbnQgb3BlcmF0aW5nIHN5c3RlbXM6DQoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGEgaHJlZj0iI21hYyI+TWFjIE9TPC9hPjxiciAvPjxhIGhyZWY9IiN3aW5kb3dzIj5XaW5kb3dzPC9hPjxiciAvPjwvcD4NCgkJPHVsPg0KCQkJCTxsaT4NCgkJCQkJCTxhIGhyZWY9IiN2aXN0YSI+V2luZG93cyA3IG9yIFZpc3RhPC9hPg0KCQkJCTwvbGk+DQoJCQkJPGxpPg0KCQkJCQkJPGEgaHJlZj0iI3dpbjgiPldpbmRvd3MgOC8xMDwvYT4NCgkJCQkJCTxiciAvPg0KCQkJCTwvbGk+DQoJCQkJPGxpPg0KCQkJCQkJPGEgaHJlZj0iI3dpbjExIj5XaW5kb3dzIDExPC9hPg0KCQkJCTwvbGk+DQoJCTwvdWw+DQoJCTxwPg0KCQkJCTxhIGhyZWY9IiNsaW51eCI+TGludXg8L2E+DQoJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJPGI+DQoJCQkJCQk8YSBuYW1lPSJtYWMiPk1hYyBPUzwvYT4NCgkJCQk8L2I+DQoJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJPGJyIC8+MS4gT3BlbiB0aGUgPGI+VGVybWluYWwuYXBwPC9iPiwgZWl0aGVyIGJ5IHN0YXJ0aW5nIHR5cGluZyBUZXJtaW5hbCBvbiB0aGUgU3BvdGxpZ2h0IG9yIGJ5IGdvaW5nIGludG8gPGI+QXBwbGljYXRpb25zPC9iPi4gDQo8YnIgLz48L3A+DQoJCTxiPg0KCQk8L2I+DQoJCTIuIEdvIHRvIDxiPjxiPlV0aWxpdGllczwvYj48L2I+IGFuZCBjbGljayA8Yj5UZXJtaW5hbDwvYj46DQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgY2xhc3M9ImtiLWltYWdlIiBzcmM9Imh0dHBzOi8vTmFtZWNoZWFwLnNpbXBsZWtiLmNvbS9TaXRlQ29udGVudHMvMi03QzIyRDUyMzZBNDU0M0VCODI3RjNCRDg5MzZFMTUzRS9tZWRpYS9jbGVhcmRuc2NhY2hlMS5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGRpdj4zLiBSdW4gb25lIG9mIHRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgY29tbWFuZHMgZGVwZW5kaW5nIG9uIHRoZSBNYWNPUyB2ZXJzaW9uIHlvdSdyZSB1c2luZyBhbmQgcHJlc3MgRW50ZXIsIHRoZW4gdHlwZSB5b3VyIHVzZXIgcGFzc3dvcmQgd2hlbiBwcm9tcHRlZDogPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PHRhYmxlIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItY29sbGFwc2U6IGNvbGxhcHNlOyB3aWR0aDogMTAwJTsiIGJvcmRlcj0iMSI+PHRib2R5Pjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9IndpZHRoOiA1MCU7Ij48c3Ryb25nPk9TIHZlcnNpb248L3N0cm9uZz48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsiPjxzdHJvbmc+Q29tbWFuZCB0byBjbGVhciBjYWNoZTwvc3Ryb25nPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJ3aWR0aDogNTAlOyI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij5PUyBYIFlvc2VtaXRlPC9zcGFuPjxiciAvPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+T1MgWCBFbCBDYXBpdGFuPC9zcGFuPjxiciAvPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+TWFjT1MgU2llcnJhIGFuZCBIaWdoIFNpZXJyYTwvc3Bhbj48YnIgLz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPk1hY09TIE1vamF2ZTwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsiPjxwPjxlbT48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPnN1ZG8ga2lsbGFsbCAtSFVQIG1ETlNSZXNwb25kZXI8L3NwYW4+PC9lbT48ZW0+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij48YnIgLz48L3NwYW4+PC9lbT48ZW0+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij48YnIgLz48L3NwYW4+PC9lbT48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPm9yPC9zcGFuPjwvcD48cD48ZW0+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij5zdWRvIGtpbGxhbGwgLUhVUCBtRE5TUmVzcG9uZGVyOyBzYXkgRE5TIGNhY2hlIGZsdXNoZWQ8L3NwYW4+PC9lbT48L3A+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9IndpZHRoOiA1MCU7Ij48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPk1hY09TIENhdGFsaW5hPC9zcGFuPjwvdGQ+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJ3aWR0aDogNTAlOyI+PGVtPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+c3VkbyBraWxsYWxsIC1IVVAgbUROU1Jlc3BvbmRlcjsgPC9zcGFuPjwvZW0+PC90ZD48L3RyPjx0cj48dGQgc3R5bGU9IndpZHRoOiA1MCU7Ij48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPk1hY09TIEJpZyBTdXI8L3NwYW4+PGJyIC8+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij5NYWNPUyBNb250ZXJleTwvc3Bhbj48YnIgLz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPk1hY09TIFNvbm9tYcKgPC9zcGFuPjxiciAvPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+TWFjT1MgU2VxdW9pYTwvc3Bhbj48YnIgLz48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPk1hY09TIFRhaG9lPC9zcGFuPjwvdGQ+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJ3aWR0aDogNTAlOyI+PGVtPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+c3VkbyBkc2NhY2hldXRpbCAtZmx1c2hjYWNoZTsgc3VkbyBraWxsYWxsIC1IVVAgbUROU1Jlc3BvbmRlcjwvc3Bhbj48L2VtPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48L3Rib2R5PjwvdGFibGU+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+PGEgbmFtZT0id2luZG93cyI+V2luZG93cyBPUzwvYT48L2I+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+QmVsb3cgeW91IGNhbiBmaW5kIGluc3RydWN0aW9ucyBvbiBob3cgdG8gY2xlYXIgbG9jYWwgRE5TIGNhY2hlIG9uIGRpZmZlcmVudCB2ZXJzaW9ucyBvZiBXaW5kb3dzIE9TLg0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz48dWw+PGxpPjxiPjxhIG5hbWU9InZpc3RhIj5XaW5kb3dzIDcgb3IgVmlzdGE8L2E+PC9iPjwvbGk+PC91bD4xLiBDbGljayBvbiB0aGUgPGI+U3RhcnQ8L2I+IGJ1dHRvbg0KDQo8aW1nIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3dpbmRvd3M3X3N0YXJ0LnBuZyIgd2lkdGg9IjM4IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjM4IiAvPi48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4yLiBDbGljayA8Yj5BbGwgUHJvZ3JhbXMgPC9iPiAmZ3Q7IDxiPkFjY2Vzc29yaWVzPC9iPiAmZ3Q7IHJpZ2h0LWNsaWNrIG9uIDxiPkNvbW1hbmQgUHJvbXB0PC9iPiBhbmQgY2hvb3NlIFJ1biBhcyBBZG1pbmlzdHJhdG9yOg0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvY2xlYXJkbnNjYWNoZTkucG5nIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjMuIEluIHRoZSBDb21tYW5kIFByb21wdCB3aW5kb3cgdHlwZSBpbiA8aT5pcGNvbmZpZyAvZmx1c2hkbnM8L2k+IGFuZCBwcmVzcyA8Yj5FbnRlcjwvYj46DQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgY2xhc3M9ImtiLWltYWdlIiBzcmM9Imh0dHBzOi8vTmFtZWNoZWFwLnNpbXBsZWtiLmNvbS9TaXRlQ29udGVudHMvMi03QzIyRDUyMzZBNDU0M0VCODI3RjNCRDg5MzZFMTUzRS9tZWRpYS9jbGVhcmRuc2NhY2hlMTAucG5nIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjQuIE9uY2UgZG9uZSwgeW91IHdpbGwgc2VlIHRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgbWVzc2FnZTogU3VjY2Vzc2Z1bGx5IGZsdXNoZWQgdGhlIEROUyBSZXNvbHZlciBDYWNoZS4NCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PHVsPjxsaT48Yj48YSBuYW1lPSJ3aW44Ij5XaW5kb3dzIDgvMTA8L2E+PGEgbmFtZT0id2luOCI+PC9hPjwvYj48L2xpPjwvdWw+PGJyIC8+VGhlIEZsdXNoIEROUyBjb21tYW5kIG9uIFdpbmRvd3MgOC8xMCBpcyB0aGUgc2FtZSBhcyBvbiBXaW5kb3dzIDcgYW5kIFZpc3RhLCB0aGUgZGlmZmVyZW5jZSBpcyBvbmx5IGluIGhvdyB0byBvcGVuIHRoZSBjb21tYW5kIHByb21wdC4NCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjEuIFByZXNzIHRoZSA8Yj5TdGFydCA8L2I+YnV0dG9uDQoNCiA8aW1nIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3dpbjhtYWlsMS5wbmciIHdpZHRoPSIyNSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIyOCIgLz4gJmd0OyA8Yj5BcHBsaWNhdGlvbnM8L2I+ICZndDsgdHlwZSA8Yj5Db21tYW5kIHByb21wdDwvYj4gaW4gdGhlIHNlYXJjaCBiYXI6IA0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvY2xlYXJkbnNjYWNoZTEyLnBuZyIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4yLiBJbiB0aGUgQ29tbWFuZCBQcm9tcHQgd2luZG93IHR5cGUgaW4gPGk+aXBjb25maWcgL2ZsdXNoZG5zPC9pPiBhbmQgcHJlc3MgPGI+RW50ZXI8L2I+Og0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvY2xlYXJkbnNjYWNoZTEzLnBuZyIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4zLiBBZnRlciB0aGUgY2FjaGUgaXMgY2xlYXJlZCwgeW91IHdpbGwgZ2V0IHRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgbWVzc2FnZTogU3VjY2Vzc2Z1bGx5IGZsdXNoZWQgdGhlIEROUyBSZXNvbHZlciBDYWNoZS4NCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PHVsPjxsaT48Yj48YSBuYW1lPSJ3aW4xMSI+V2luZG93cyAxMTwvYT48L2I+PC9saT48L3VsPjEuIFByZXNzIHRoZSA8Yj5TdGFydDwvYj4gYnV0dG9uICZndDsgPGI+QXBwbGljYXRpb25zPC9iPiAmZ3Q7IHR5cGUgPGI+Q29tbWFuZCBQcm9tcHQ8L2I+IGluIHRoZSBzZWFyY2ggYmFyOjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgY2xhc3M9ImtiLWltYWdlIiBzcmM9Imh0dHBzOi8vTmFtZWNoZWFwLnNpbXBsZWtiLmNvbS9TaXRlQ29udGVudHMvMi03QzIyRDUyMzZBNDU0M0VCODI3RjNCRDg5MzZFMTUzRS9tZWRpYS9jbGVhciBkbnMgY2FjaGVfMS5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+Mi4gIEluIHRoZSBDb21tYW5kIFByb21wdCB3aW5kb3csIHR5cGUgaW4gPGk+aXBjb25maWcgL2ZsdXNoZG5zPC9pPiBhbmQgcHJlc3MgRW50ZXI6PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2NsZWFyIGRucyBjYWNoZV8yLnBuZyIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4zLkFmdGVyIHRoZSBjYWNoZSBpcyBjbGVhcmVkLCB5b3Ugd2lsbCBnZXQgdGhlIGZvbGxvd2luZyBtZXNzYWdlOiA8aT5TdWNjZXNzZnVsbHkgZmx1c2hlZCB0aGUgRE5TIFJlc29sdmVyIENhY2hlPC9pPi4NCg0KDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiPjxhIG5hbWU9ImxpbnV4Ij5MaW51eCBPUzwvYT48L2I+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+RGlmZmVyZW50IExpbnV4IGRpc3RyaWJ1dGlvbnMgdXNlIGRpZmZlcmVudCBETlMgcmVzb2x2ZXJzIChlLmcuLCA8Y29kZT5zeXN0ZW1kLXJlc29sdmVkLCBuc2NkLCBkbnNtYXNxLDwvY29kZT4gb3IgPGNvZGU+TmV0d29ya01hbmFnZXI8L2NvZGU+KS48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4NCg0KVG8gY2hlY2sgd2hpY2ggRE5TIHNlcnZpY2UgeW91ciBzeXN0ZW0gdXNlcywgcnVuIHRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgY29tbWFuZCBpbiB5b3VyIGZhdm9yaXRlIHRlcm1pbmFsL3NoZWxsIGFwcGxpY2F0aW9uOg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGk+cHMgYXV4IHwgZ3JlcCAtRSAic3lzdGVtZC1yZXNvbHZlZHxuc2NkfGRuc21hc3EiPC9pPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPg0KDQpZb3Ugd2lsbCBzZWUgdGhlIG5hbWUgb2YgdGhlIEROUyByZXNvbHZlciB1c2VkIG9uIHlvdXIgTGludXggc3lzdGVtIGluIHRoZSBvdXRwdXQgb2YgdGhpcyBjb21tYW5kLiBJdCBtYXkgYmUgPGNvZGU+c3lzdGVtZC1yZXNvbHZlZDwvY29kZT4sIDxjb2RlPm5zY2Q8L2NvZGU+LCBvciA8Y29kZT5kbnNtYXNxPC9jb2RlPi48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4NCg0KSWYgbm9uZSBvZiB0aG9zZSBhcHBlYXIsIHlvdXIgc3lzdGVtIG1pZ2h0IHJlbHkgb24gPGNvZGU+TmV0d29ya01hbmFnZXI8L2NvZGU+IG9yIHlvdXIgYnJvd3NlcuKAmXMgRE5TIGNhY2hlLjxiciAvPjxiciAvPg0KDQpBZnRlciB5b3Uga25vdyB3aGljaCBETlMgcmVzb2x2ZXIgaXMgdXNlZCBpbiB5b3VyIHN5c3RlbSwgY2hvb3NlIHRoZSBjb3JyZWN0IGNvbW1hbmQgZm9yIGNsZWFyaW5nIGEgbG9jYWwgRE5TIGNhY2hlIGZvciB0aGlzIHJlc29sdmVyOjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjx0YWJsZSBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLWNvbGxhcHNlOiBjb2xsYXBzZTsgd2lkdGg6IDEwMCU7IGhlaWdodDogOTBweDsiIGJvcmRlcj0iMSI+PHRib2R5Pjx0ciBzdHlsZT0iaGVpZ2h0OiAzOHB4OyI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJ3aWR0aDogNTAlOyBoZWlnaHQ6IDM4cHg7Ij48c3Ryb25nPlJlc29sdmVyPC9zdHJvbmc+PC90ZD48dGQgc3R5bGU9IndpZHRoOiA1MCU7IGhlaWdodDogMzhweDsiPjxzdHJvbmc+Q29tbWFuZCB0byBjbGVhciBjYWNoZTwvc3Ryb25nPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHIgc3R5bGU9ImhlaWdodDogMTBweDsiPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsgaGVpZ2h0OiAxMHB4OyI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij5zeXN0ZW1kLXJlc29sdmVkPC9zcGFuPjwvdGQ+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJ3aWR0aDogNTAlOyBoZWlnaHQ6IDEwcHg7Ij48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPjxpPnN1ZG8gc3lzdGVtZC1yZXNvbHZlIC0tZmx1c2gtY2FjaGVzPC9pPjwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyIHN0eWxlPSJoZWlnaHQ6IDE4cHg7Ij48dGQgc3R5bGU9IndpZHRoOiA1MCU7IGhlaWdodDogMThweDsiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+cmVzb2x2ZWN0bDwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsgaGVpZ2h0OiAxOHB4OyI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij48aT5zdWRvIHJlc29sdmVjdGwgZmx1c2gtY2FjaGVzPC9pPjwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyIHN0eWxlPSJoZWlnaHQ6IDI0cHg7Ij48dGQgc3R5bGU9IndpZHRoOiA1MCU7IGhlaWdodDogMjRweDsiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+bnNjZDwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsgaGVpZ2h0OiAyNHB4OyI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij48aT5zdWRvIHN5c3RlbWN0bCByZXN0YXJ0IG5zY2QNCg0KPC9pPjwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjwvdHI+PHRyPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+ZG5zbWFzcTwvc3Bhbj48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPjxiciAvPjwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+PGk+c3VkbyBzeXN0ZW1jdGwgcmVzdGFydCBkbnNtYXNxDQo8L2k+PC9zcGFuPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48dHI+PHRkIHN0eWxlPSJ3aWR0aDogNTAlOyI+PHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiA0MDA7Ij5OZXR3b3JrTWFuYWdlcjwvc3Bhbj48c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IDQwMDsiPjxiciAvPjwvc3Bhbj48L3RkPjx0ZCBzdHlsZT0id2lkdGg6IDUwJTsiPjxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogNDAwOyI+PGk+TmV0d29ya01hbmFnZXINCnN1ZG8gc3lzdGVtY3RsIHJlc3RhcnQgTmV0d29ya01hbmFnZXINCg0KDQo8L2k+PC9zcGFuPjwvdGQ+PC90cj48L3Rib2R5PjwvdGFibGU+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+WW91IGNhbiBjaGVjayBpZiB0aGUgY2FjaGUgd2FzIGZsdXNoZWQgc3VjY2Vzc2Z1bGx5IHVzaW5nIHRoaXMgY29tbWFuZDo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aT4kIHN1ZG8gc3lzdGVtZC1yZXNvbHZlIC0tc3RhdGlzdGljczwvaT48YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvY2xlYXIgZG5zIGNhY2hlXzMucG5nIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPg0KSWYgeW91IHNlZSBhIDxiPnplcm88L2I+IGJ5IHRoZSA8Yj5DdXJyZW50IENhY2hlIFNpemU8L2I+LCB5b3UgaGF2ZSBzdWNjZXNzZnVsbHkgZmx1c2hlZCB5b3VyIHN5c3RlbSdzIGNhY2hlLjxiciAvPjwvZGl2PjxkaXY+PGJyIC8+PC9kaXY+PGRpdj48YnIgLz48L2Rpdj5UaGF0J3MgaXQhPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+DQrCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgIDxiciAvPsKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoCBOZWVkIGFueSBoZWxwPyBDb250YWN0IG91ciA8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL2hlbHAtY2VudGVyLyI+SGVscERlc2s8L2E+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PHA+PC9wPjxwPjwvcD4=","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"2025-10-10T14:28:47.0000000","LiveDateTime":"1754-02-02T00:00:00.0000000","CreatedDateTime":"2008-08-06T10:32:55.0000000","ApprovalDatetime":"2015-06-29T02:02:21.0000000","RequestCount":113379,"MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false,"RatingValue":3,"CategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"}],"AssociatedCategories":[{"CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks","CategoryDisplayName":"HostingTips & Tricks"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":74,"Tag":" dns"},{"TagId":20538,"Tag":" mac"},{"TagId":21234,"Tag":" clear"},{"TagId":25338,"Tag":" windows"},{"TagId":83318,"Tag":" dns cache"}],"RelatedArticles":[],"AssociatedMedias":[],"PreferredCategoryId":0,"RootParentCategoryName":"","RootParentCategoryId":0},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategorybycategoryid:\"{\\\"categoryId\\\":2194}\"":{"body":{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"Parent_Category_Name":"Hosting","FriendlyId":null,"ApprovedYN":true,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"CreatedDateTime":"06/13/2013 08:34:05","CurrentCategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"}],"RelatedCategories":[],"AssociatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":9207,"Title":"How to clear cache in different browsers (Mac OS)","ArticleName":"How to clear cache in different browsers (Mac OS)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/06/2025"},{"ArticleId":9366,"Title":"Errors 500, 502, 503, 504 and 508. Reasons and ways of fixing","ArticleName":"Errors 500, 502, 503, 504 and 508. Reasons and ways of fixing","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/19/2024"},{"ArticleId":9777,"Title":"How to use TCP traceroute","ArticleName":"How to use TCP traceroute","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/20/2023"},{"ArticleId":9997,"Title":"What is hotlinking and how to prevent it","ArticleName":"What is hotlinking and how to prevent it","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/09/2021"},{"ArticleId":10078,"Title":"How to do a hard refresh in Chrome, Firefox and IE?","ArticleName":"How to do a hard refresh in Chrome, Firefox and IE?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/29/2018"},{"ArticleId":10094,"Title":"How to create and download website backup automatically","ArticleName":"How to create and download website backup automatically","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/27/2025"},{"ArticleId":10222,"Title":"How to configure a dedicated IP address to show the website","ArticleName":"How to configure a dedicated IP address to show the website","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/15/2024"},{"ArticleId":10227,"Title":"How to work with a scan report","ArticleName":"How to work with a scan report","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/11/2024"},{"ArticleId":10266,"Title":"How to connect to remote storage on CentOS server","ArticleName":"How to connect to remote storage on CentOS server","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/23/2020"},{"ArticleId":10329,"Title":"How to enable Under attack mode for the domain in Cloudflare account","ArticleName":"How to enable Under attack mode for the domain in Cloudflare account","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/07/2025"},{"ArticleId":10345,"Title":"How to install CAPTCHA on your website","ArticleName":"How to install CAPTCHA on your website","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/25/2020"},{"ArticleId":10591,"Title":"How to fix the \"DNS server not responding\" error","ArticleName":"How to fix the \"DNS server not responding\" error","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/11/2023"},{"ArticleId":10647,"Title":"How to Fix Error 524","ArticleName":"How to Fix Error 524","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/12/2023"},{"ArticleId":9206,"Title":"How to clear cache in different browsers","ArticleName":"How to clear cache in different browsers","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"08/03/2022"},{"ArticleId":9208,"Title":"How to clear cache in different browsers (Mobile OS)","ArticleName":"How to clear cache in different browsers (Mobile OS)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"08/03/2022"},{"ArticleId":9209,"Title":"How to clear cache in different browsers (Windows)","ArticleName":"How to clear cache in different browsers (Windows)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/05/2025"},{"ArticleId":9658,"Title":"How to use the Browser Console","ArticleName":"How to use the Browser Console","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/14/2021"},{"ArticleId":397,"Title":"How to clear local DNS cache","ArticleName":"How to clear local DNS cache","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/10/2025"},{"ArticleId":858,"Title":"How to get email headers","ArticleName":"How to get email headers","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"06/12/2025"},{"ArticleId":9242,"Title":"How to prevent your hosting account from being hacked","ArticleName":"How to prevent your hosting account from being hacked","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/07/2025"},{"ArticleId":9696,"Title":"How to protect your content from being copied","ArticleName":"How to protect your content from being copied","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/09/2021"},{"ArticleId":9541,"Title":"How to optimize hosting account space","ArticleName":"How to optimize hosting account space","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/16/2024"},{"ArticleId":9667,"Title":"What are Traceroute, Ping, Telnet and Nslookup commands?","ArticleName":"What are Traceroute, Ping, Telnet and Nslookup commands?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/05/2024"},{"ArticleId":9568,"Title":"My website is down: what to do?","ArticleName":"My website is down: what to do?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"06/25/2024"},{"ArticleId":9610,"Title":"What to do when I got an email 'Malicious Attempt to Access Your Hosting Account is Detected'","ArticleName":"What to do when I got an email 'Malicious Attempt to Access Your Hosting Account is Detected'","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/07/2025"},{"ArticleId":9351,"Title":"\"Deceptive site ahead\" warning - what to do","ArticleName":"\"Deceptive site ahead\" warning - what to do","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/11/2024"}],"AssociatedTags":[],"CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategories:\"{\\\"parentCategoryId\\\":0,\\\"getTree\\\":true}\"":{"body":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/cloud-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2228,"CategoryName":"Apps","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/easywp-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2239,"CategoryName":"EasyWP","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2254,"CategoryName":"Domains How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2255,"CategoryName":"Hosting How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2257,"CategoryName":"Sales & Payments How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2258,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2262,"CategoryName":"EasyWP How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://download.namecheap.com/assets/img/domainvault-red@2x.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2289,"CategoryName":"Domain Vault","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/support-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":5,"CategoryName":"General & Support","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/savings-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2200,"CategoryName":"Checkout & Billing","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/reseller-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/protection-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":37,"CategoryName":"Domain Privacy Protection","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/status-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2209,"CategoryName":"Domain Transfers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/server-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/email-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/security-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/performance-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":9,"CategoryName":"My Account","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/affiliates-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":55,"CategoryName":"Affiliates","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/tools-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2211,"CategoryName":"API & Resellers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/timer-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2212,"CategoryName":"Legacy Products","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/premiumdns-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2231,"CategoryName":"PremiumDNS","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://static.nc-img.com/live-resource/icons/knowledgebase/fastVPN_icon-150px.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2265,"CategoryName":"FastVPN","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}],"status":200,"statusText":"OK"}}
This guide describes how to clear local DNS cache on different operating systems:
Mac OS
Windows
Linux
Mac OS
1. Open the Terminal.app, either by starting typing Terminal on the Spotlight or by going into Applications.
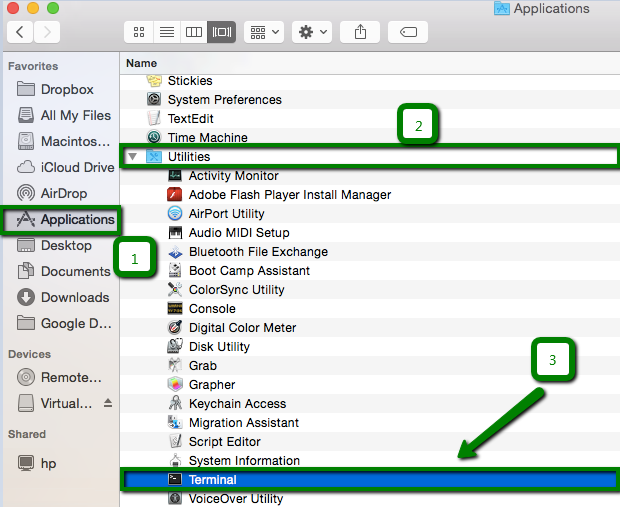
| OS version | Command to clear cache |
| OS X Yosemite OS X El Capitan MacOS Sierra and High Sierra MacOS Mojave | sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; say DNS cache flushed |
| MacOS Catalina | sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; |
| MacOS Big Sur MacOS Monterey MacOS Sonoma MacOS Sequoia MacOS Tahoe | sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder |
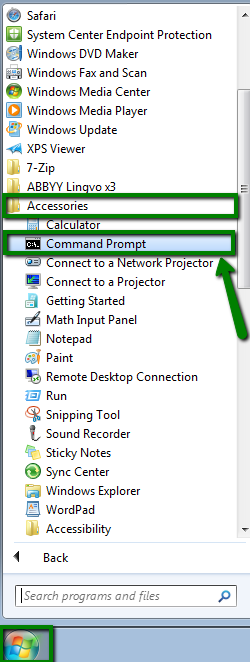
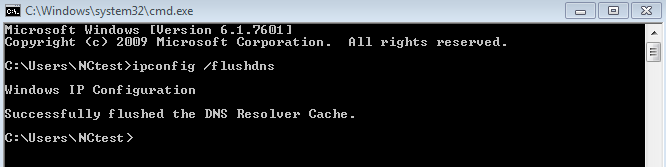
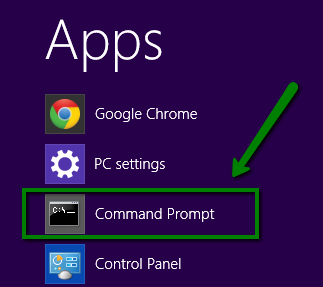
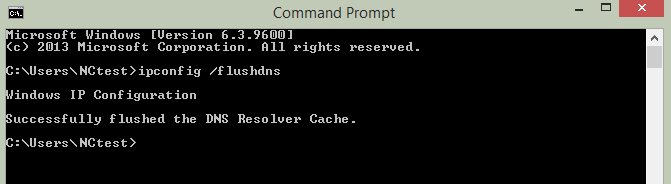


systemd-resolved, nscd, dnsmasq, or NetworkManager).systemd-resolved, nscd, or dnsmasq.NetworkManager or your browser’s DNS cache.| Resolver | Command to clear cache |
| systemd-resolved | sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches |
| resolvectl | sudo resolvectl flush-caches |
| nscd | sudo systemctl restart nscd |
| dnsmasq | sudo systemctl restart dnsmasq |
| NetworkManager | NetworkManager sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager |

Need help? We're always here for you.